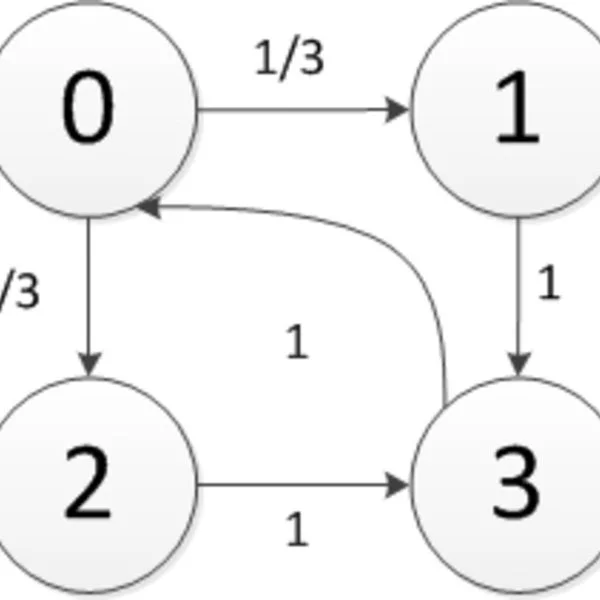
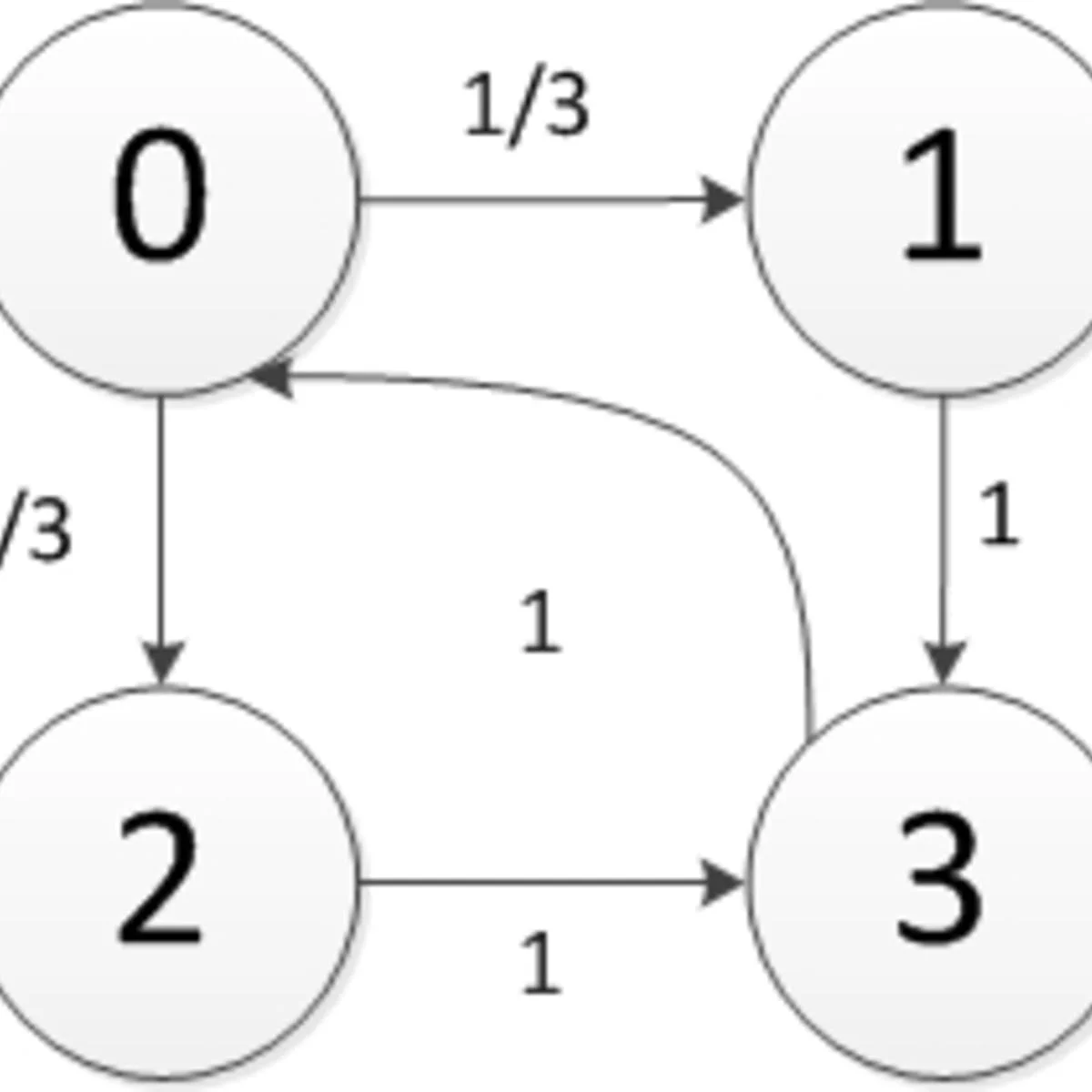
The integration of ICT (information and communications technology) in different applications is rapidly increasing in e.g. Embedded and Cyber physical systems, Communication protocols and Transportation systems. Hence, their reliability and dependability increasingly depends on software. Defects can be fatal and extremely costly (with regards to mass–production of products and safety–critical systems). First, a model of the real system has to be built. In the simplest case, the model reflects all possible states that the system can reach and all possible transitions between states in a (labelled) State Transition System. When adding probabilities and discrete time to the model, we are dealing with so–called Discrete–time Markov chains which in turn can be extended with continuous timing to Continuous–time Markov chains. Both formalisms have been used widely for modeling and performance and dependability evaluation of computer and communication systems in a wide variety of domains. These formalisms are well understood, mathematically attractive while at the same time flexible enough to model complex systems. Model checking focuses on the qualitative evaluation of the model. As formal verification method, model checking analyzes the functionality of the system model. A property that needs to be analyzed has to be specified in a logic with consistent syntax and …
Instructor Details
Courses : 1
Specification: Quantitative Model Checking
|
4 reviews for Quantitative Model Checking
Add a review Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
| Price | Free |
|---|---|
| Provider | |
| Duration | 22 hours |
| Year | 2017 |
| Level | Intermediate |
| Language | English |
| Certificate | Yes |
| Quizzes | Yes |
FREE



Mario A G S –
Very good course!!!
Joseph V –
The lectures on Coursera are nice, but please remove to cringe parts (any outside shot video material). Overall the course is very bad because the tele lectures are very bad quality and thus does not motivate you at all to keep track of the course during the period. Recommendation: Ditch tele lectures all together and give actual bonus points for completing Coursera parts on time.
ElissaHu –
difficult in week4&week5, but interesting
Carl H –
Lectures are rushed and not explained well. Discussion forms seem to be filled with “Is there inaccuracy in in quiz X”. Here is a direct quote from one of the discussions “I actually didn’t use the formula from the lecture but from the cited paper by Baier et. al. same stuff. works for 11, doesn’t for 12”. Granted that the subject matter this course covers is difficult, I feel like this course makes it harder rather than easier. I wouldn’t recommend it to anyone.